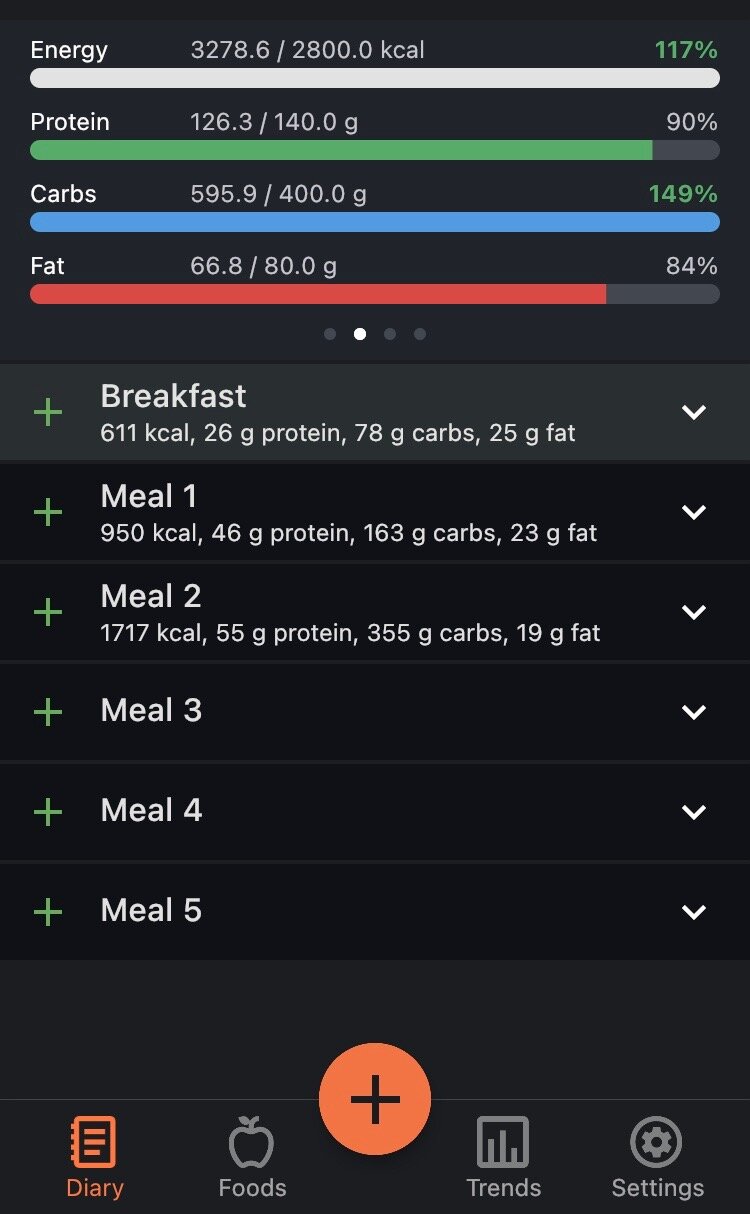
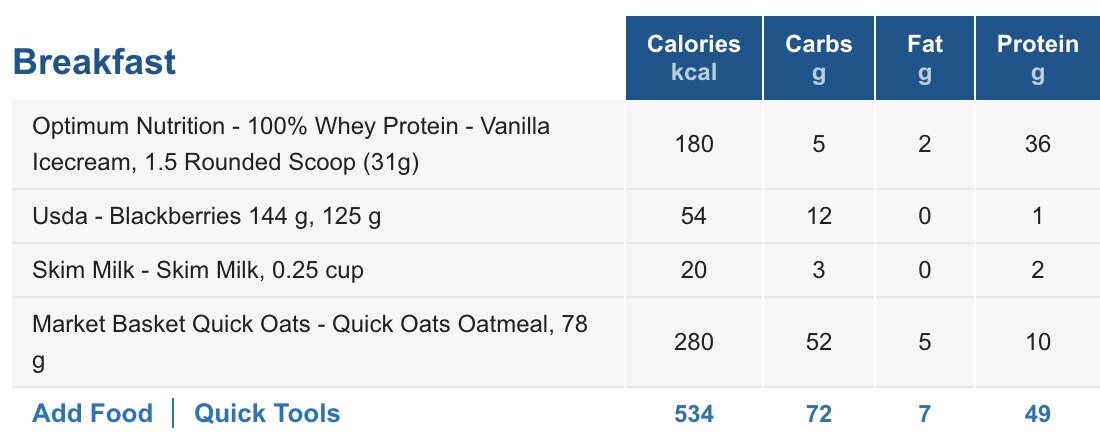
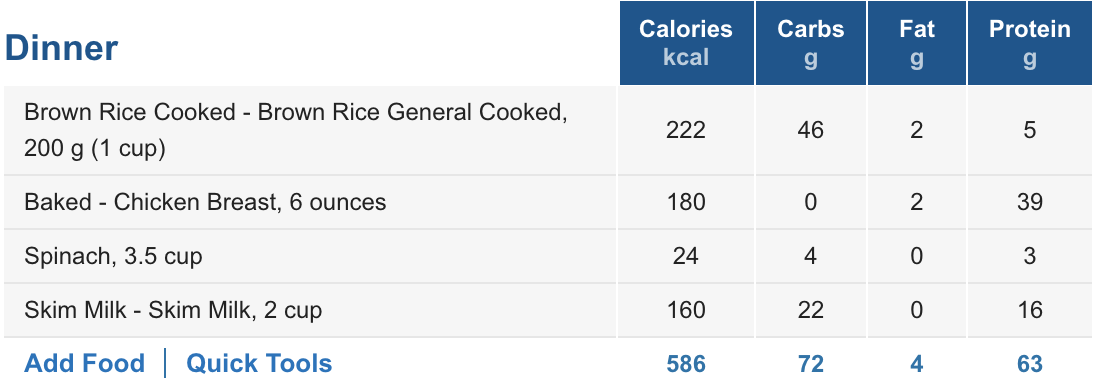
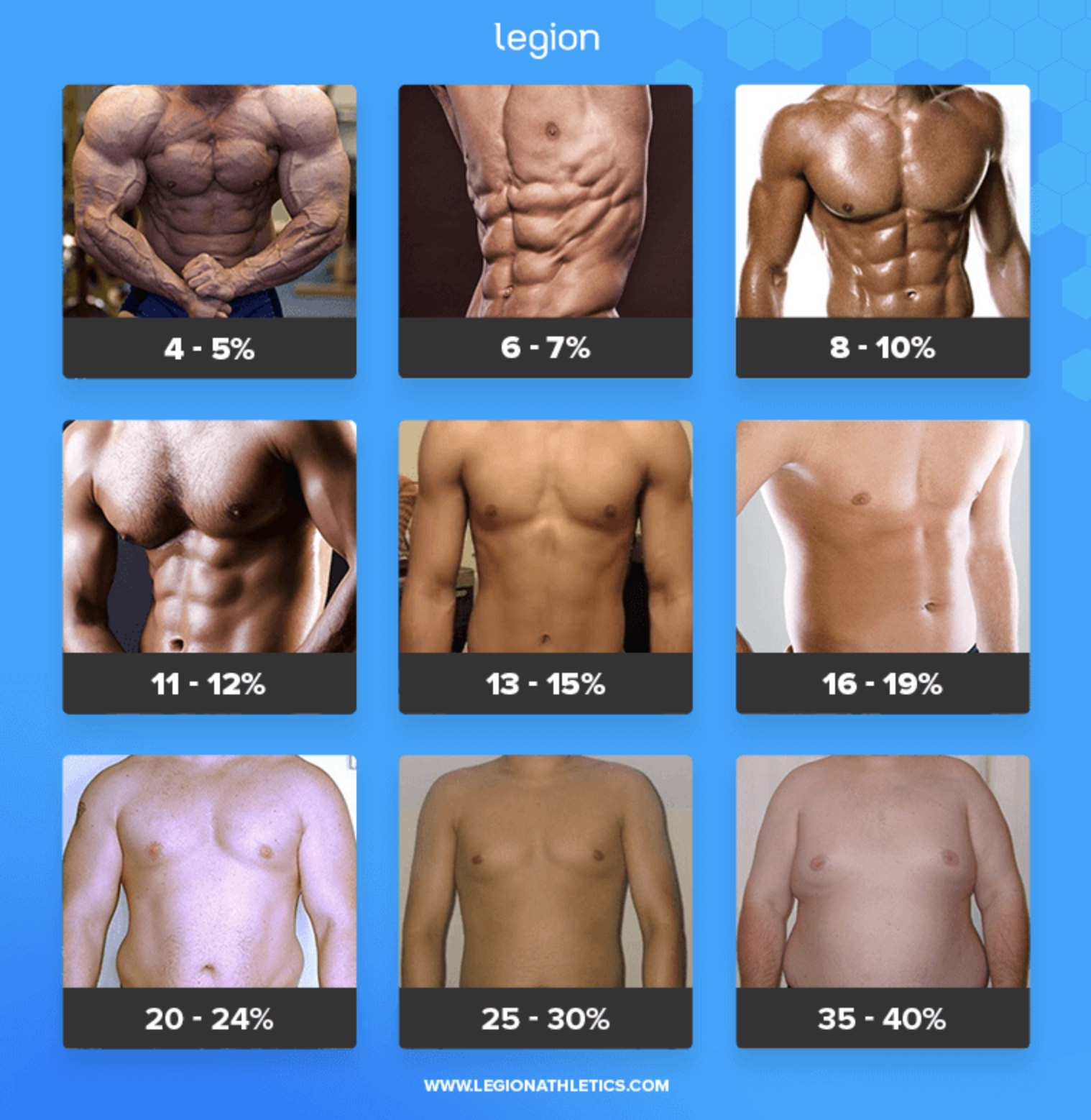
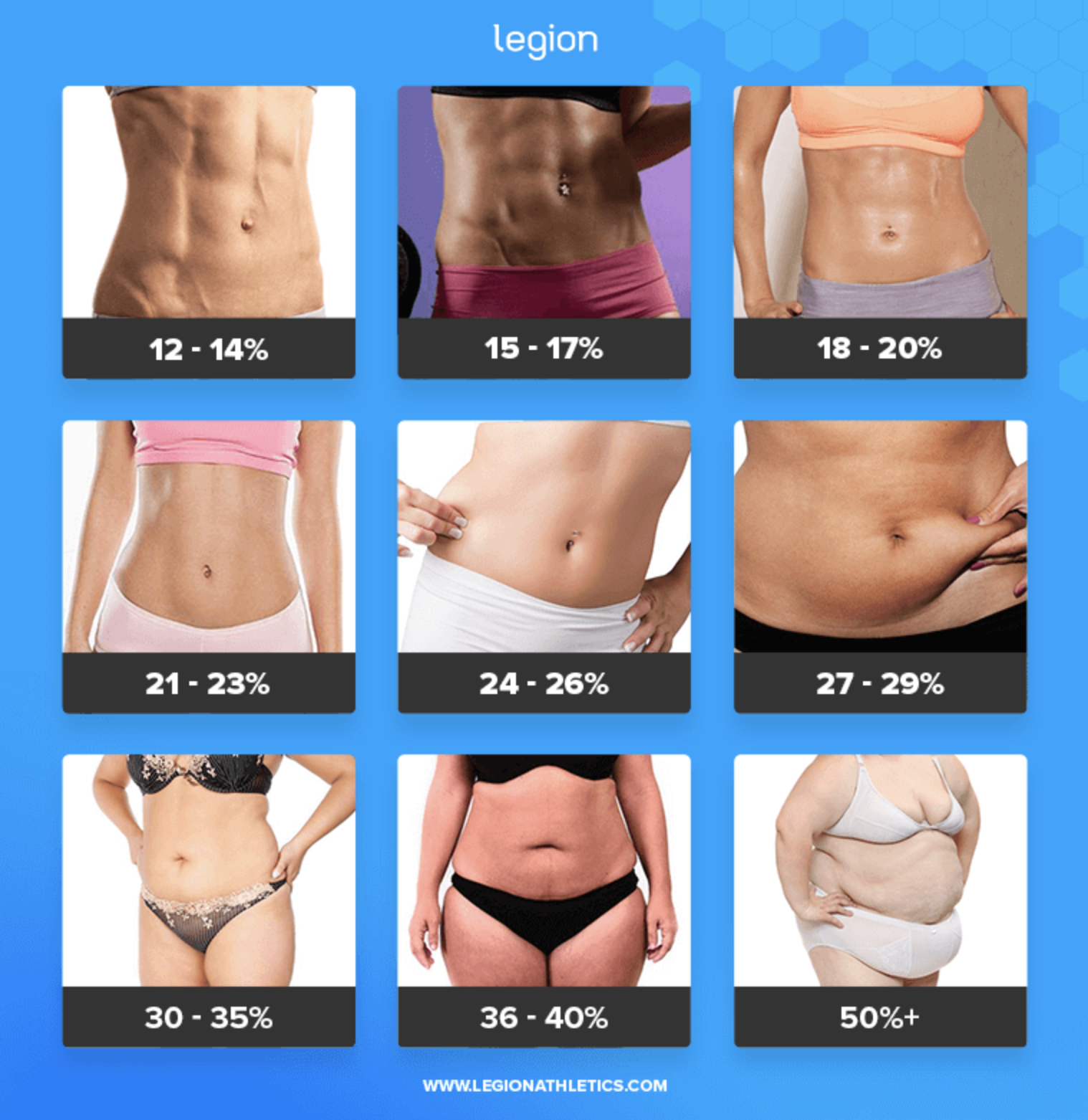
To be honest with you, this article originally began as a personal note to myself I cyber-scribbled into my iPhone one day on a flight from Denver to St. Louis.
For quite some time, I had been making my body recomposition journey way too complicated, and I had become the poster child of self-inflicted paralysis by analysis.
And although ultimately my desire to understand every known detail about evidence-based body recomposition had fueled a lot of personal growth for me, I was starting to realize that it had also prevented me from taking my best strides at times.
I remember rewriting my own training programs over and over again thinking, “Finally! This is the perfect mesocycle for muscle growth,” just to rewrite it once more in a few days.
I remember thinking tirelessly about the “perfect” number of sets I should be doing each week and wondering fruitlessly if I should be counting drop sets as full sets or a half sets.
And I remember being hyper-focused on getting six “hits” of muscle protein synthesis per day to the extent that I was setting 150-minute timers on my phone so I’d know when to guzzle down my next serving of shredded chicken and half of a plain bagel.
I once even bought raw, cartoned egg whites and drank them in the car during a road tip because I was unwilling to miss an opportunity to “stimulate muscle growth.”
As the saying goes, I was missing the forest for the trees.
I had become so entrenched in the details that I had failed to look up and remember the grander narrative of what it meant to improve my body composition sustainably over time.
Does any of this sound relatable?
If so, I want to share with you what I wrote in that small note on my phone that day with the hope of helping you refocus on what matters most for a successful body recomposition endeavor.
5 Tips for Getting Back to Basics for an Improved Body Recomposition
1. remember that Calories matter most for fat loss, but your health and livelihood probably matter too.
It's so easy to overcomplicate this, but it really is true that you can get shredded to the bone while paying attention to calories and nothing else.
Just take a look at anyone who’s ever been stranded at sea on a handcrafted life raft like Chuck Noland and his spherical confidant Wilson circa 2000.
And in some sense, this is both good news and bad news.
It’s good news in that weight loss has now become very simple. If you consume fewer calories than you expend, you’ll lose weight.
But it’s bad news in that it becomes increasingly tempting to think of foods exclusively in terms of their caloric density and nothing else.
So now there’s really no good argument for ever eating an avocado or a handful of almonds over a Rice Krispies Treat because avocados have nearly three times as many calories than their marshmallow friends.
And yet most of us understand that avocados are probably the healthier option when pitted against an ultra-processed dessert made by a curious clan of animated elves.
Are you seeing how this can quickly become complicated?
At some point, the question we all have to ask ourselves is this:
To what extent will we nuance our understanding of calorie balance for a fat loss effort with our best understanding of how to eat for optimal health?
And so even though you could consume brownie batter flavored whey protein, Rice Krispie Treats, and peanut butter toward a leaner and meaner physique, it begs a few questions.
Would that be good for your health? Would you lose muscle mass? Would you be performing at your best on a diet of ultra-processed foods and somewhat “empty” calories?
Would your skin look the same? Would your hair be healthy? Would you be thriving sexually?
Would your sleep quality be high? Would you have energy throughout the day to invest in the relationships that matter most to you?
As I alluded to before, I ignored nearly all of those questions for a very long time in the name of caloric over-obsession and nothing else.
Did I get lean? Absolutely. But did I do so at the expense of my overall health? I believe so.
So to mitigate the risk of overcomplicating my first point in an article written to encourage people not to overcomplicate things, the main takeaway here is this:
Being in a calorie deficit is king for fat loss, but you’ll want to make sure you’ve thought through the health and wellness ramifications of your dietary pattern as well.
In fact, I think it’s similar to playing a game of chess.
In some undeniable sense, the king is the most important piece on the board. You cannot win without protecting him. Your own king, in this case, is your application of calorie balance.
But there are other important pieces on the board as well: the queen, your rooks, the bishops and the knights, and even the seemingly insignificant pawns that can become queens if you shepherd them well and guide safely beyond enemy lines.
We might consider these your overall health, your energy levels, your sleep quality, and your sex drive (among many others).
The key to becoming a great chess player is being able to command all of your pieces toward a unified goal while considering the greater context of the ultimate task at hand.
Will you be able to consider all of the pieces and how they can help you achieve your goal?
Or will you fail to see the bigger picture and miss the forest for the trees?
2. Don’t forget that training quality is the most important thing for building muscle.
I screwed this up for a long time too because I was searching for the “perfect” dietary pattern like it was the lost city of Atlantis.
In other words, I was placing a disproportionate amount of attention on my diet to give me the look I wanted instead of the quality of my training. I was incessantly tweaking something with the hopes of optimizing my physique just that much more.
And in doing so, I neglected my training quality.
In some sense, this this is the overcompensation for my first point in this article, and it’s a great example of how you can make a good thing a bad thing.
If you focus too much on the quality of your diet, you might forget that you actually have to train intelligently and intensely in the gym to build the muscle you want.
The point here is to settle into a dietary pattern that is supported by evidence for positive physique improvements and then eat habitually while you train with purpose.
The less time you can spend overthinking your diet the better.
For example, don’t waste time and energy wondering if eating 20 extra grams of carbohydrates from bananas versus berries during your pre-workout meal is going to yield you an extra 1% of muscle gain over the next five years.
Just get in the gym and train hard!
In summary, if a major component of your body recomposition goal is to grow bigger muscles, be sure to focus on high-quality training above all else.
3. Don’t overcomplicate your protein intake at the expense of other macronutrients.
This is another mistake I was making.
I had gotten overly focused on consuming excessive amounts of protein at the expense of food quality and overall food diversity.
As I mentioned before, there was a time when I would estimate that nearly 80% of my calories were coming from Fresh toast doused in sugar-free maple syrup and bowls upon bowls of teriyaki chicken.
Why?
Because they allowed me to “hit my macros” with convenience and ease.
Not only this, but I was convinced that five protein feeds per day must be better than four, and six must be even better than five. In doing so, I manipulated myself psychologically to believe that I “didn’t want my goals badly enough” when I only made time to eat three times per day.
Do I regret it? Absolutely.
Unfortunately, that season of eating was characterized by low energy levels and overall lethargy, digestive discomfort, and delayed post-workout recovery.
And even more unfortunately, I see now that choosing to eat that way had actually suppressed some of my greater values of health and vitality in favor of a “protein at all costs” mindset.
In short, my encouragement to you here is not to become protein-obsessed at the expense of a more well-rounded nutritional profile.
Instead, focus on eating an adequate amount of daily protein that supports your goal, and then maximize your intake of colorful plant foods as you approach your daily caloric target.
In an attempt to lead by example, I’ve now adopted a completely plant-based diet that is rich in lean protein sources, fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
I feel better than ever, I eat much less protein than I used to (while eating way more carbohydrates and fats), and I’ve only continued to see steady muscle and strength gains since making that change in May 2021.
4. don’t stress about meals you can’t track perfectly.
As much as I enjoy the systematic fat loss outcomes of tracking food, I had come to realize that there were many times in life when tracking a meal just wasn’t worth the cost.
For example, one of my really good friends made me a delicious curry the other night.
If you've been around the macro-tracking block a few times, you know that curry isn't very tracker-friendly.
It's nearly impossible to know exactly how much of this vegetable or that vegetable was in your particular serving, and the sauce is always a caloric mystery.
This can make eating out with a friends a nightmare for people with orthorexic tendencies.
And this can be the case with many homemade meals like pastas, casseroles, and slow cooker meals.
Rather than stressing about it (like I would have in the past), I embraced the meal and simply kept my portion size reasonable and limited myself to one plate.
And I couldn't have been happier about it.
I didn't strain the relationship by being a high-maintenance guest, we were able to enjoy a delicious meal together without distraction, and I left feeling completely in control of my diet and physique.
So remember that not every meal in life will be trackable.
Learn to know when to relax and rely on mindful eating habits like portion sizes and eating to fullness without excess.
5. never forget that Sustainability wins in the end.
I mostly hate the phrase "do what works for you" because it always seems wildly unhelpful and conversationally lazy.
But this is one scenario where I think it works really well as long as we offer a brief explanation of exactly what we mean.
As it pertains to feeling more confident in your birthday suit, you’re still going to have to do all of the evidence-based things I’m always teasing out in all of my IVRY articles, but there are going to be small ways here and there that you can tweak your own lifestyle in unique ways for long-term body recomposition success.
For example, when dieting for fat loss, I used to eat a big breakfast and skip lunch in favor of a small snack in the afternoon and a bigger dinner while other people might prefer to fast until 1PM and then have their first large meal.
We're both generally still playing by all of the same rules of calorie balance, but we're manipulating those rules to our advantage based on our own preferences.
Does that make sense?
In my observations, this is a hallmark feature of all successful dieters - the ability to modify and nuance minor lifestyle behaviors in way that is rhythmic, repeatably, and sustainable for them.
Can I take it a bit further?
To be super frank, I'm not a proponent of transformations that people can't maintain long-term.
After having done this for awhile, I know how to sniff out a transformation photo of someone who crash dieted and destroyed their health to win an online “transformation challenge.”
Most people can starve themselves for eight weeks and "look hot" for a wedding. Most people can do super keto for three months and lose 30 pounds. Most people can suffer through P90X once to reveal a blurry six-pack and a plump, worm-like vein in their left bicep.
But what most people can't do is keep the weight off.
My point? Sustainability wins in the end.
Do yourself a favor and remind yourself to play the long game.
Summary
When you’re passionate about improving your body composition, overcomplicating things can be an easy trap to fall into.
Remember that calorie balance is most important for weight loss, but it’s probably a good idea to consider your health and wellness as well. The key is to find a balance.
Never forget that training quality matters most for building muscle. Try not to let other aspects of the process distract you from executing a well-designed training plan with a high level of focus and intensity.
Avoid overcomplicating your protein intake. Once you’ve identified an adequate amount of protein to eat on a daily basis, maximize your consumption of healthy carbohydrates and fats within your caloric target.
Come to terms with the fact that you won’t be able to track every meal to the gram. In those unavoidable situations, eat mindfully and do your best to enjoy the moment stress free. You don’t have to keep a food scale in your back pocket at all times to be lean and muscular.
Lastly, remember that sustainability is the name of the game. If overcomplicating any aspect of your body recomposition journey is preventing you from getting the results you want, you’d be smart to reconsider your plan in favor of something more sustainable.
As always, I really enjoyed writing this article.
If you found it helpful, consider sending it to a friend!
Until next time,
-Andrew